Korea Med Tour in South Korea
Traditional Korean Medicine vs Western Medicine differ in philosophy, diagnosis, and treatment. Western medicine targets specific diseases using lab tests, drugs, and surgery, while Traditional Korean Medicine focuses on restoring systemic balance through acupuncture, herbal medicine, and pattern identification. Both are regulated and often used together in Korea.
Traditional Korean Medicine (TKM) and Western medicine differ primarily in their philosophy, diagnostic approach, and treatment strategy. TKM focuses on restoring balance in the body using herbal medicine, acupuncture, and holistic pattern identification, while Western medicine emphasizes disease-specific diagnosis, laboratory testing, pharmaceuticals, and surgery based on biomedical science. Both systems are evidence-informed, regulated in Korea, and often used together in integrative care models.
Table of Contents

Why This Comparison Matters in 2026
As global patients increasingly seek personalized, preventive, and integrative healthcare, many ask: What is the real difference between Traditional Korean Medicine and Western medicine—and which one should I choose?
In countries like South Korea, both systems are fully licensed and operate in parallel. Patients may receive acupuncture for chronic pain while also taking prescription medication, or combine herbal therapy with post-surgical rehabilitation. Understanding the philosophical, scientific, and clinical differences between these two medical frameworks helps patients make informed decisions—especially in medical tourism and chronic disease management contexts.
This guide explains the differences clearly, based on current 2026 medical standards, regulatory frameworks, and real-world clinical practice.
1. Foundational Philosophy
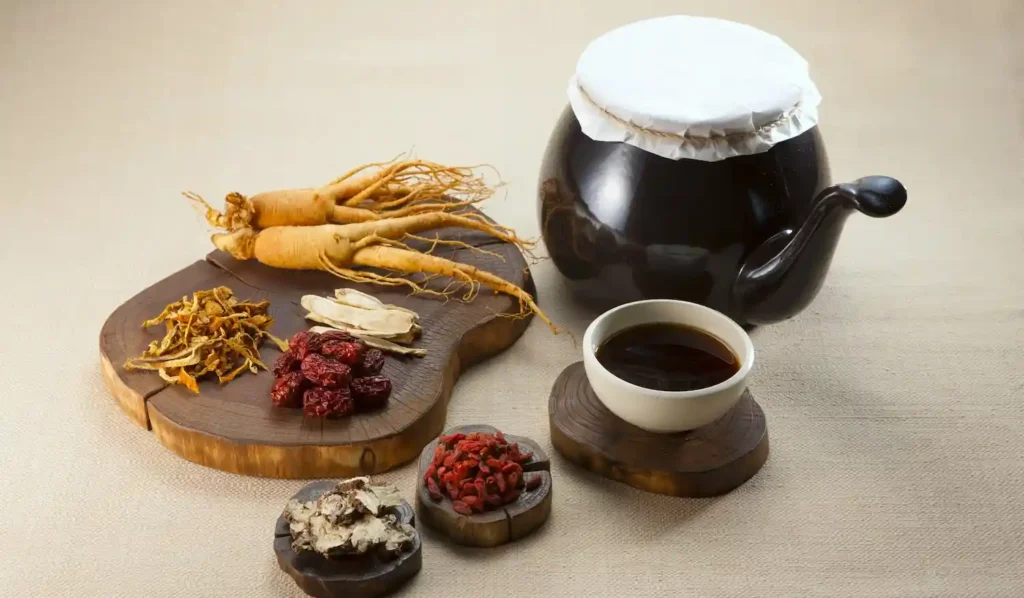
Traditional Korean Medicine (TKM)
Traditional Korean Medicine, rooted in East Asian medical theory, views the body as an interconnected system regulated by:
- Qi (vital energy)
- Yin and Yang balance
- Five-element theory
- Organ-meridian systems
Illness is interpreted as a pattern imbalance, not simply a localized pathology. For example, migraine may be diagnosed as “liver yang rising” rather than just a neurological condition.
Treatment aims to:
- Restore systemic balance
- Improve constitutional resilience
- Address root causes and contributing patterns
Western Medicine
Western medicine (biomedicine or allopathic medicine) is based on:
- Anatomy and physiology
- Pathology and microbiology
- Evidence-based pharmacology
- Molecular and genetic science
Illness is typically defined by:
- Identifiable pathology
- Measurable biomarkers
- Imaging findings
- Laboratory abnormalities
Treatment targets:
- The specific disease process
- Identified pathogens or structural problems
- Biochemical pathways
2. Diagnostic Approach: Pattern vs Pathology
One of the most significant differences lies in diagnosis.
TKM Diagnosis
Traditional Korean Medicine relies on:
- Pulse diagnosis
- Tongue inspection
- Abdominal palpation
- Symptom pattern differentiation
- Constitutional analysis (e.g., Sasang typology)
Two patients with identical Western diagnoses may receive different TKM treatments depending on their constitutional pattern.
Example:
Two patients with irritable bowel syndrome:
- Patient A: Cold-type deficiency pattern
- Patient B: Heat-excess pattern
Treatment strategies differ completely, even though the Western diagnosis is the same.
Western Medical Diagnosis
Western medicine uses:
- Blood tests
- Imaging (MRI, CT, ultrasound)
- Biopsy
- Pathogen identification
- Standardized diagnostic criteria
The goal is reproducibility and objective measurement.
For example:
- Diabetes diagnosed by HbA1c levels
- Pneumonia confirmed by chest X-ray
- Cancer staged via imaging and pathology
3. Treatment Modalities Compared
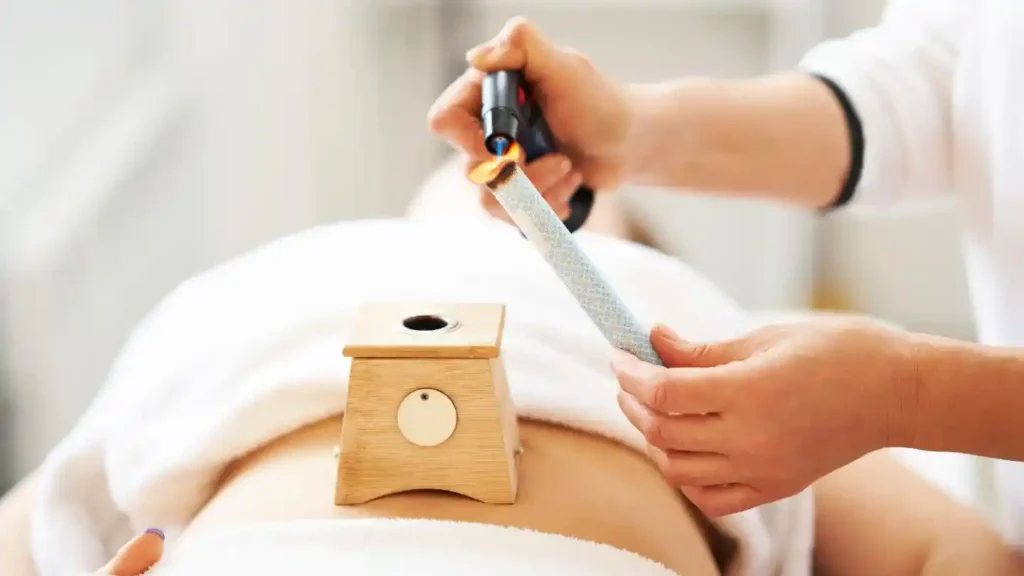
Traditional Korean Medicine Treatments
- Acupuncture
- Herbal medicine formulations
- Moxibustion
- Cupping therapy
- Chuna manual therapy (Korean spinal manipulation)
- Pharmacopuncture (herbal extract injections)
TKM treatments often aim to:
- Stimulate self-healing
- Modulate immune response
- Improve circulation
- Regulate autonomic nervous system balance
Modern Korean TKM hospitals integrate:
- Digital X-ray imaging
- Standardized herbal extraction processes
- GMP-certified herbal manufacturing
Western Medicine Treatments
- Prescription medications
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Physical therapy
- Vaccination
Western interventions are typically:
- Rapid-acting
- Protocol-based
- Standardized
- Condition-specific
For acute emergencies (e.g., heart attack, stroke, trauma), Western medicine is essential.
4. Scientific Evidence: How Do They Compare?

Western Medicine Evidence Model
Western medicine uses:
- Randomized controlled trials (RCTs)
- Meta-analyses
- Clinical guidelines
- FDA-style drug approval processes
Strength:
- High standardization
- Strong regulatory oversight
- Predictable pharmacological effects
Limitation:
- May under-address chronic functional syndromes without clear pathology.
Evidence in Traditional Korean Medicine
Research in TKM includes:
- Clinical trials on acupuncture for chronic pain
- Studies on herbal anti-inflammatory compounds
- Neuroimaging studies on acupuncture effects
- Government-funded integrative research
For example:
- Acupuncture has demonstrated effectiveness for chronic low back pain and osteoarthritis in systematic reviews.
- Certain herbal formulations show immune-modulating and anti-inflammatory effects in peer-reviewed research.
However:
- Herbal formulations are individualized, making large-scale standardization challenging.
- Mechanisms are still being clarified through modern biomedical research.
In South Korea, TKM doctors undergo six years of medical education and national licensing exams. Herbal medicines are regulated by the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.
5. Acute vs Chronic Conditions
Western Medicine Strengths:
- Emergency medicine
- Trauma care
- Infectious disease
- Advanced surgical interventions
- Oncology
TKM Strengths:
- Chronic pain
- Functional digestive disorders
- Stress-related disorders
- Insomnia
- Menstrual irregularities
- Preventive and constitutional care
Real-world example:
A patient recovering from lumbar disc surgery may:
- Use Western surgery for structural correction
- Undergo acupuncture and herbal therapy for post-operative inflammation and nerve recovery
Integrative models often provide the best outcomes.
6. Risk and Safety Profiles
Western Medicine Risks
- Medication side effects
- Surgical complications
- Drug interactions
- Antibiotic resistance
TKM Risks
- Herbal-drug interactions
- Improper herbal sourcing
- Overstimulation from acupuncture (rare but possible)
In regulated Korean medical institutions:
- Herbs are quality-controlled
- Practitioners are licensed
- Cross-referral between systems is common
Patients should disclose all medications to both providers to prevent interactions.
7. Treatment Duration and Expectations
Western medicine often aims for:
- Rapid symptom suppression
- Clear treatment endpoints
TKM often emphasizes:
- Gradual systemic rebalancing
- Longer treatment courses
- Preventive care
For example:
Hypertension in Western medicine:
- Managed with antihypertensive medication.
In TKM:
- May focus on stress regulation, liver yang balance, and circulatory improvement alongside lifestyle modification.
They are not mutually exclusive.
8. Education and Licensing in Korea
In South Korea:
- Western physicians attend medical school and complete residency training.
- TKM doctors attend accredited Korean medicine universities and pass national board exams.
Both are government-regulated professionals, but they cannot practice each other’s discipline unless dual-licensed.
This parallel licensing system is unique compared to many countries where traditional medicine is less formally regulated.
9. When Should You Choose Each?
Choose Western Medicine When:
- You have an emergency
- You need surgery
- You have confirmed infection
- You require cancer treatment
- Diagnostic clarity is required urgently
Consider TKM When:
- Chronic pain persists despite medication
- You seek preventive health optimization
- Stress-related symptoms dominate
- You prefer non-pharmacologic approaches
- You want adjunctive rehabilitation
Consider Integrative Care When:
- Managing autoimmune disorders
- Post-surgical recovery
- Long-term inflammatory conditions
- Functional syndromes with unclear pathology
10. Common Misconceptions
Myth 1: Traditional medicine is unscientific.
Modern Korean Medicine includes laboratory research, standardized herbal extraction, and peer-reviewed studies.
Myth 2: Western medicine ignores prevention.
Preventive medicine and lifestyle medicine are expanding rapidly within Western systems.
Myth 3: You must choose one system.
In Korea, many patients safely use both under professional supervision.
Final Takeaway
Traditional Korean Medicine and Western medicine are not opposing forces—they are different medical frameworks built on distinct theoretical foundations.
Western medicine excels in acute, life-threatening, and structural disease management. Traditional Korean Medicine focuses on systemic balance, chronic conditions, and preventive care. In South Korea’s regulated dual-medical system, patients often benefit from integrative strategies that combine the strengths of both.
In 2026, informed healthcare decisions require understanding not only what each system treats, but how and why it approaches disease differently. The most effective care model is often individualized, evidence-informed, and supervised by licensed professionals who prioritize patient safety and long-term outcomes.

FAQs
What is the main difference between Traditional Korean Medicine vs Western Medicine?
The main difference between Traditional Korean Medicine vs Western Medicine lies in diagnostic philosophy and treatment strategy. Western medicine identifies specific pathology using lab tests and imaging, while Traditional Korean Medicine evaluates holistic imbalance and treats using acupuncture, herbal medicine, and integrative healthcare approaches in Korea.
Is Korean acupuncture more effective than Western treatment?
Korean acupuncture vs Western treatment depends on the condition. Western medicine is superior for acute emergencies and infections, while Korean acupuncture is widely used for chronic pain, stress disorders, and musculoskeletal conditions as part of holistic medicine in Korea.
Can Traditional Korean Medicine and Western Medicine be combined?
Yes. Traditional Korean Medicine vs Western Medicine are often combined in Korea’s integrative healthcare system. Patients may use pharmaceuticals for acute management while receiving acupuncture or herbal therapy for rehabilitation and long-term balance.
Which is safer: Traditional Korean Medicine or Western Medicine?
Both Traditional Korean Medicine vs Western Medicine are safe when practiced by licensed professionals. Western medicine carries pharmaceutical and surgical risks, while holistic medicine in Korea requires proper monitoring for herbal-drug interactions.
Is Traditional Korean Medicine scientifically proven?
Research continues to evaluate Traditional Korean Medicine vs Western Medicine under modern standards. Korean acupuncture and certain herbal formulations have clinical studies supporting their use, particularly for chronic pain and inflammatory conditions within integrative healthcare Korea models.
Korea Med Tour – Trusted Blog for Medical Tourism in Korea
Your Trusted Guide to Medical Tourism in Korea
Korea Med Tour is a leading medical tourism blog dedicated to providing accurate, up-to-date, and trustworthy information for international patients seeking healthcare services in South Korea. Our mission is to help travelers make informed decisions about their medical care while exploring the benefits of Korea’s world-class healthcare system.
With a focus on transparency, reliability, and expert-backed content, Korea Med Tour covers a wide range of medical fields including dermatology, plastic surgery, dental care, health checkups, and wellness services. We aim to empower readers with clear guidance on treatment options, clinic selection, cost expectations, and travel logistics.
What We Offer
- Clinic & Hospital Reviews – In-depth articles and reviews of Korea’s top medical facilities.
- Procedure Guides – Step-by-step explanations of popular medical treatments and aesthetic procedures.
- Patient Stories & Testimonials – Real experiences from international patients visiting Korea.
- Medical Travel Tips – Advice on planning your trip, accommodations, language support, and insurance.
- Health & Wellness Insights – Information on preventive care, checkups, and holistic treatments.
Why Choose Korea Med Tour
- Trusted Information – All content is based on verified sources, expert insights, and up-to-date research.
- Patient-Centered Guidance – We prioritize clarity, safety, and realistic expectations for all readers.
- International-Friendly Resources – Content is tailored for global patients, with practical tips for navigating Korea’s healthcare system.
Explore Korea Med Tour: https://KoreaMedTour.com
Your guide to safe, informed, and seamless medical travel in Korea.